- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Network Access Control
- Re: The Windows user remotes into a workstation with RDS/Remote Desktop that is on a different VLAN ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 09:55 AM - edited 01-29-2020 09:55 AM
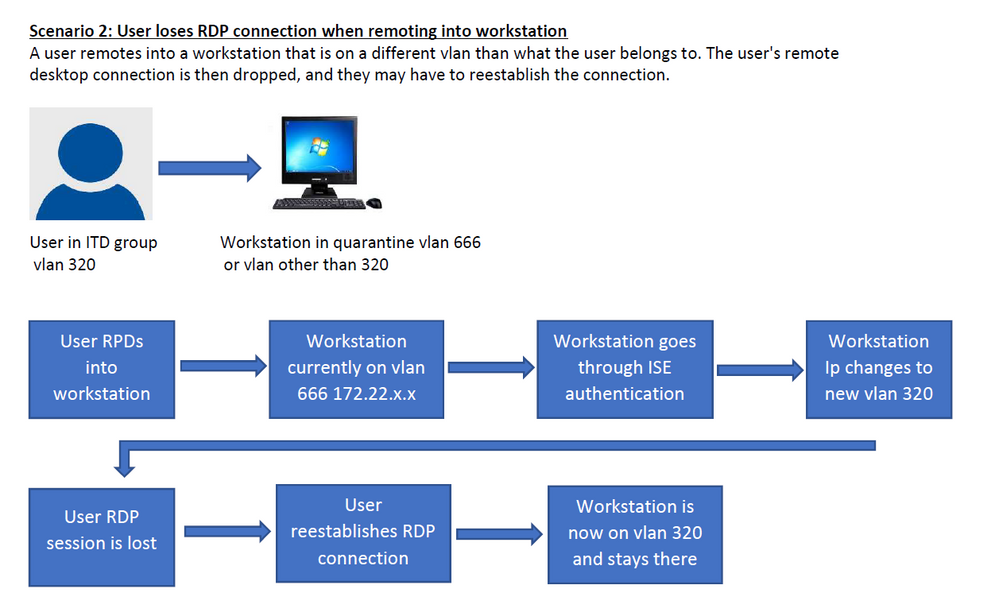
The Windows user remotes into a workstation with RDS/Remote Desktop that is on a different VLAN than what the user belongs to. The user's remote desktop connection is then dropped, and they have to reestablish RDS/Remote Desktop the connection. Please provide some configuration changes and solutions to this scenario.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Identity Services Engine (ISE)
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 10:23 AM
What behavior are you wanting it to do? Do you want it to stay in its current VLAN (i.e. 666)? Or do you want it to change based on the user but NOT drop the RDP connection? The challenge with that is anytime you change VLAN's, you are also changing subnets. The IP on the PC changes and the RDP connection drops. There is really no way around that.
I personally don't recommend doing any VLAN assignments on Windows machines because of this issue. A normal user logging in and switching VLAN's can cause GPOs, login scripts, drive mappings, etc. to all fail because of the change of IP address. Downloadable ACL's are more appropriate. I also really don't recommend doing user authentication unless you absolutely need to differentiate access based on who the user is.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 11:45 AM
@Colby LeMaire wrote:
What behavior are you wanting it to do? Do you want it to stay in its current VLAN (i.e. 666)? Or do you want it to change based on the user but NOT drop the RDP connection? The challenge with that is anytime you change VLAN's, you are also changing subnets. The IP on the PC changes and the RDP connection drops. There is really no way around that.
I personally don't recommend doing any VLAN assignments on Windows machines because of this issue. A normal user logging in and switching VLAN's can cause GPOs, login scripts, drive mappings, etc. to all fail because of the change of IP address. Downloadable ACL's are more appropriate. I also really don't recommend doing user authentication unless you absolutely need to differentiate access based on who the user is.
Agree, nothing besides switching to ACLs or start using Scalable Group Tags (SGT) which are even more recommended
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 10:23 AM
What behavior are you wanting it to do? Do you want it to stay in its current VLAN (i.e. 666)? Or do you want it to change based on the user but NOT drop the RDP connection? The challenge with that is anytime you change VLAN's, you are also changing subnets. The IP on the PC changes and the RDP connection drops. There is really no way around that.
I personally don't recommend doing any VLAN assignments on Windows machines because of this issue. A normal user logging in and switching VLAN's can cause GPOs, login scripts, drive mappings, etc. to all fail because of the change of IP address. Downloadable ACL's are more appropriate. I also really don't recommend doing user authentication unless you absolutely need to differentiate access based on who the user is.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 10:44 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 11:06 AM
Yes, that would be expected behavior as I explained in my earlier response. Whether the reconnect happens automatically or the user has to connect again manually is likely dependent on how quickly Dynamic DNS is updated to the PC's new IP address. As long as it happens before the RDP timeout, then the connection can re-establish.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-29-2020 11:45 AM
@Colby LeMaire wrote:
What behavior are you wanting it to do? Do you want it to stay in its current VLAN (i.e. 666)? Or do you want it to change based on the user but NOT drop the RDP connection? The challenge with that is anytime you change VLAN's, you are also changing subnets. The IP on the PC changes and the RDP connection drops. There is really no way around that.
I personally don't recommend doing any VLAN assignments on Windows machines because of this issue. A normal user logging in and switching VLAN's can cause GPOs, login scripts, drive mappings, etc. to all fail because of the change of IP address. Downloadable ACL's are more appropriate. I also really don't recommend doing user authentication unless you absolutely need to differentiate access based on who the user is.
Agree, nothing besides switching to ACLs or start using Scalable Group Tags (SGT) which are even more recommended
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide



